A comparison of therapeutic stimulation methods: ECT, TMS, tDCS, DBS, SCS, and VNS

ECT, TMS, TDCS, DBS, SCS, and VNS are all abbreviations of stimulation methods used to treat various psychiatric and neurological conditions. But what do they actually do, and how do they differ from one another? In this article, we will review each method and establish the main differences among them.
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
ECT stands for Electroconvulsive therapy. It is a noninvasive neuromodulation method that uses a strong (approx. 800mA up) electric current to induce an epileptic seizure in the brain, aiming to reset the normal biological balance in the brain. The current is given using externally placed electrodes while the patient is under general anaesthesia and supervised by a clinician, anaesthesiologist, and trained ECT nurses.
ECT usually has a high success rate, but is primarily given in severe cases of unipolar and bipolar psychotic and suicidal depression, where milder forms of treatment have already failed. ECT is also used for treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Results are generally seen after approximately 2 weeks of treatments (approx. 6 sessions).
ECT is generally considered safe, with the most significant risks being anaesthesia-related. However, there is a risk of memory loss and cardiac arrest. Common but non-serious side effects of ECT include confusion, nausea, headache, and jaw and muscle pain.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
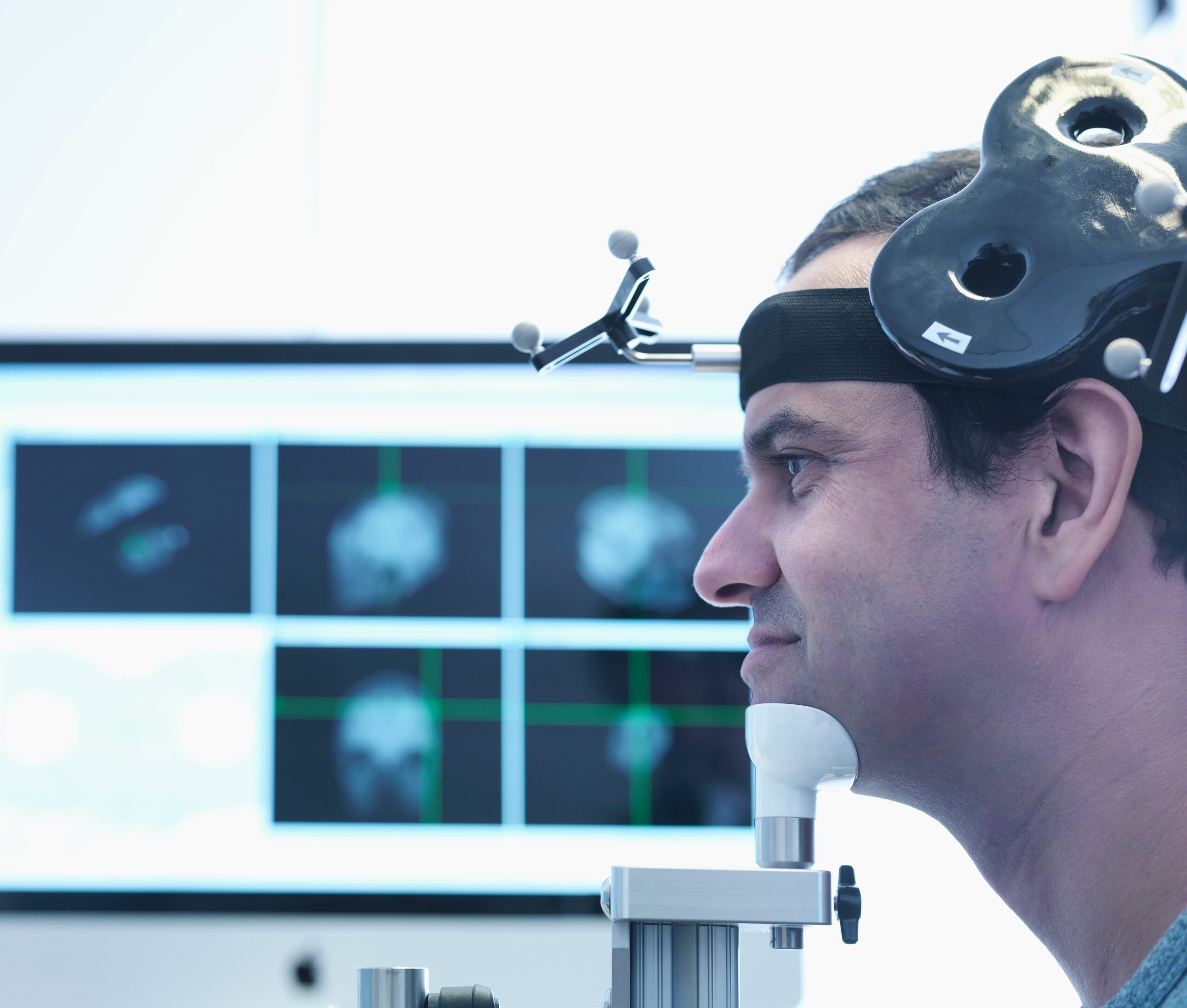
TMS stands for Transcranial magnetic stimulation. It is a noninvasive neuromodulation method that uses magnetic pulses to create electric current in targeted areas of the brain. The current affects brain plasticity by stimulating neurons to discharge “action potentials,” which are used as communicative signals inside the brain. TMS is given using an electromagnetic coil and is given at a hospital under the supervision of a clinician.
TMS is FDA-approved for and used to treat moderate and severe depression. The treatment consists of 20-30 visits to the hospital during a period of 4-6 weeks.
TMS is regarded as safe; however, there is a slight risk for seizures, which is why supervision by a clinician is required. Non-serious side effects include discomfort during stimulation, headache, light-headedness, and hearing loss.
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS)
 tDCS stands for Transcranial direct current stimulation. It is a non-invasive neuromodulation method that uses a weak (typically 2mA) electric current to stimulate targeted areas of the brain. The stimulation increases or decreases (depending on the aim) the likelihood of neurons to discharge “action potentials” (i.e., communicative brain signals). In tDCS, the current is delivered to the brain from a small, portable battery-driven device via two electrodes. A treatment course involves five sessions a week for 4–6 weeks.
tDCS stands for Transcranial direct current stimulation. It is a non-invasive neuromodulation method that uses a weak (typically 2mA) electric current to stimulate targeted areas of the brain. The stimulation increases or decreases (depending on the aim) the likelihood of neurons to discharge “action potentials” (i.e., communicative brain signals). In tDCS, the current is delivered to the brain from a small, portable battery-driven device via two electrodes. A treatment course involves five sessions a week for 4–6 weeks.
tDCS is used to treat a variety of psychological and neurological disorders, depression, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain.
tDCS is regarded as a safe treatment method and does not cause any serious adverse effects. Non-serious side effects include mild headache, an itching sensation, and redness in the stimulated area.
tDCS is the treatment method offered by Sooma for depression (Sooma Depression Therapy, indicated for Major Depressive Disorder) and chronic pain (Sooma Pain Therapy, indicated for Fibromyalgia and chronic neuropathic pain).
Deep brain stimulation (DBS)
DBS stands for Deep brain stimulation. It is an invasive neuromodulation method in which a stimulator, electrodes, and wires connecting the stimulator and electrodes are surgically implanted into the body. The stimulator is placed in the chest area and sends out electric pulses through the electrodes, which are placed inside the targeted brain areas. The stimulator is controlled using a remote control, and the amount of stimulation is customised for the patient’s condition.
DBS is primarily used to treat movement disorders, and is FDA-approved for Parkinson’s disease, Essential tremor, and Dystonia. It is also FDA-approved for Obsessive-compulsive disorder and Epilepsy.
DBS carries the usual risks related to invasive surgery and post-surgery recovery. Side effects from the stimulation can include tingling sensations, muscle tightness, and issues with vision, speech, or balance. The simulator is battery-powered and can be either non-rechargeable, in which case it needs to be surgically replaced every 2-5 years, or rechargeable, in which case it needs to be charged weekly and surgically replaced after approximately 8 years.
Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS)
SCS stands for Spinal Cord Stimulation. It is an invasive neuromodulation method where a stimulator, electrodes, and wires connecting the stimulator and electrodes are surgically placed inside the body. The stimulator is implanted below the waist in the buttock area. It sends electric pulses through the electrodes inserted into the spinal cord to reach the targeted nerves. The stimulator is controlled using a remote control, and the type of stimulation (low-frequency current vs. high-frequency pulses) and the target area are customised to the patient’s condition.
SCS is used to treat chronic pain, as the electric pulses interfere with and mask the pain signals sent from the affected part of the body to the brain. It is FDA-approved for Failed back surgery syndrome, Complex Regional Pain Syndrome, Intractable angina, and visceral abdominal and perineal pain.
SCS carries the usual risks related to invasive surgery and post-surgery recovery. Side effects from the stimulation include an unpleasant tingling sensation. The stimulator is battery-powered. Non-rechargeable batteries need to be surgically replaced every 2-5 years, while rechargeable batteries need to be recharged daily and surgically replaced after 8-10 years.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
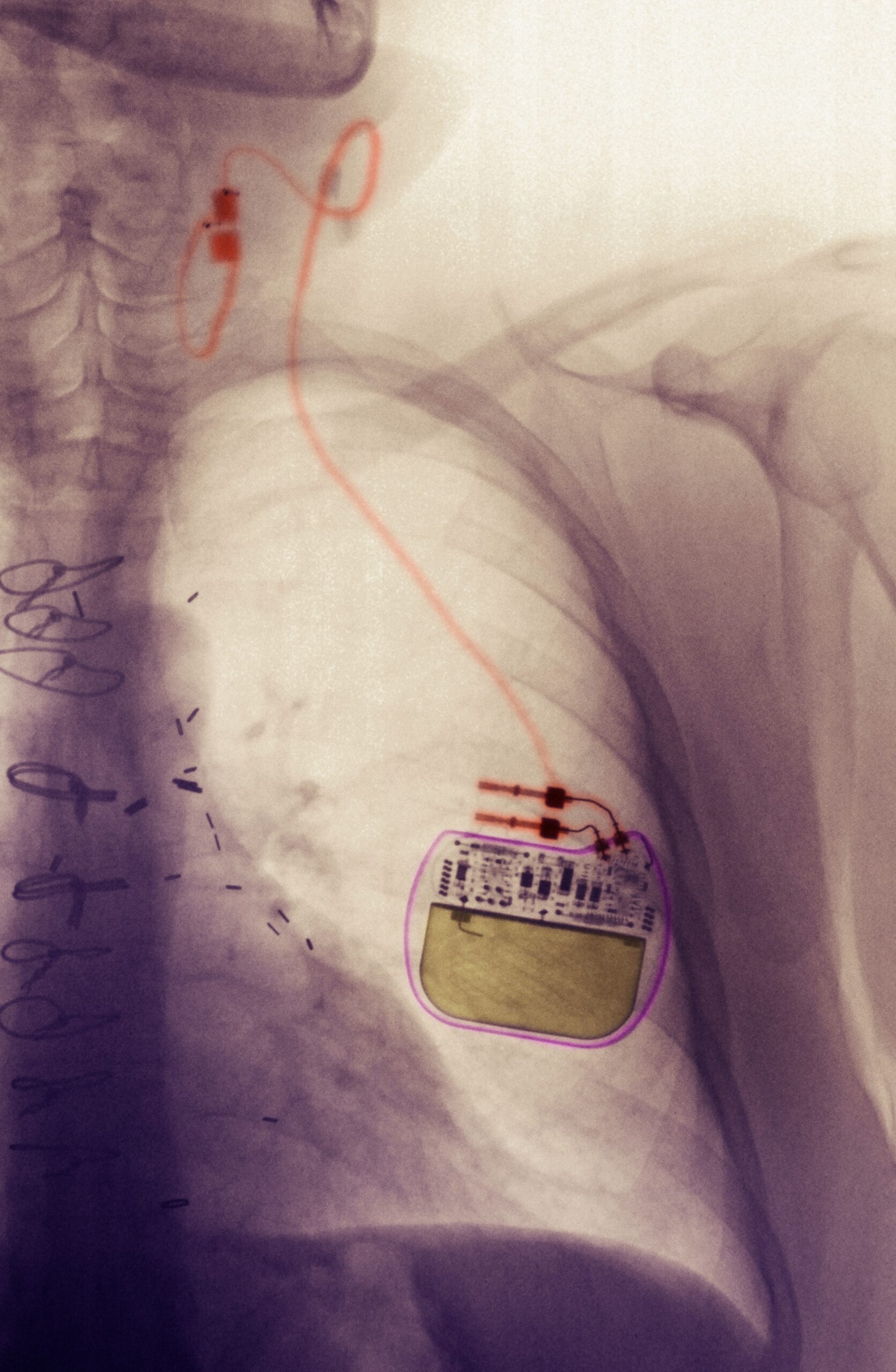
VNS stands for Vagus Nerve Stimulation. It is an invasive neuromodulation method that, as the name suggests, involves stimulating the Vagus nerve. Each person has two vagus nerves, which run from the brainstem through the neck and chest to the abdomen. In VNS, a small stimulator is implanted under the skin in the chest area, with wires that connect to the left vagus nerve, stimulating it with electrical impulses. Reacting to the stimulation, the vagus nerve sends signals to the brain.
VNS is FDA-approved for and used to treat epilepsy and depression when these conditions are otherwise drug- and treatment-resistant.
VNS carries the usual risks related to invasive surgery and post-surgery recovery. Side effects from the stimulation can present as coughing, hoarseness, voice changes, shortness of breath, throat pain, a tingling sensation, headache, and difficulty swallowing.
Latest news

TGA approves Sooma’s at-home brain stimulation for depression in Australia
Read more
Sooma Medical Announces Pivotal FDA IDE Clinical Trial for At-Home Brain Stimulation Device for Depression Treatment
Read more
Sooma Pioneers the Integration of Brain Stimulation into Primary Care, Improving Access to Early-Stage Depression Treatment
Read more